The eyelid is one of the most delicate regions of the body. Numerous glands are present in the eyelid area to maintain lubrication of the eyes. Because of its intricate and delicate structure, this area is prone to many types of infections. White bump on eyelid usually occurs when the oil glands present in the eyelid become clogged and inflamed. These bumps may remain as small lesions, which are hardly visible or swell and become painful depending upon the cause of the infection. Apart from stye, there are other types of infections of the eye that can result in bumps on eyelids.
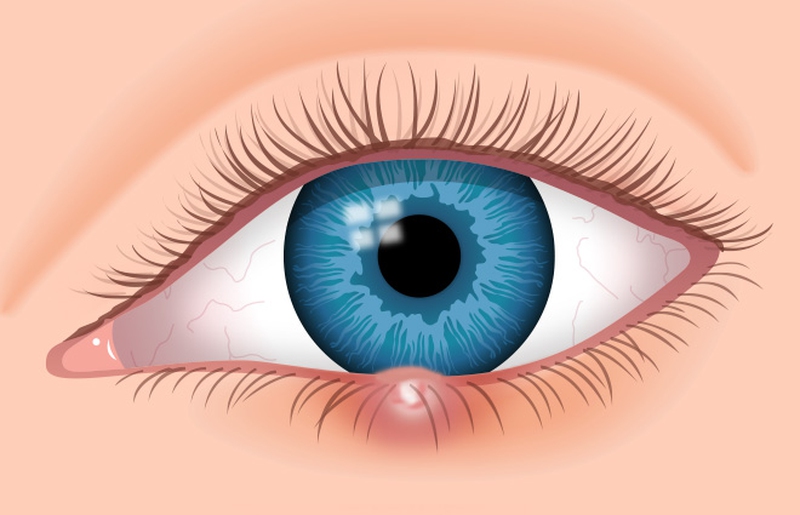
What Are the Causes of White Bumps on Eyelids?
Stye
The stye is usually caused by infection with Staphylococcus bacteria. These bacteria are part of the normal microflora of the eyelid and are typically undisruptive. However, they multiply in number uncontrollably once the bacterial growth is encouraged by external and internal factors. They infect the oil producing glands of the eyelids. The infection manifests itself as a swollen, red and tender area on the eyelid with a white bump on its center.
Chalazion
Another cause of white bumps on eyelids, chalazion is a cyst that is formed when the meibomian gland present in the tarsal plate becomes clogged. Under normal circumstances, a sticky substance is secreted by this sebaceous gland that assists in moisturizing the eyelashes. Sometimes, the duct of the sebaceous gland gets blocked leading to the clogging of the gland by sebum. A white bump develops in the area as an inflammatory response to the sebum. The bump, which is painful initially, becomes painless as it continues to enlarge. The bump may cause blurring of vision as it may distort the natural structure of the cornea. Chalazion is normally confused with stye; however, unlike stye, it is not a result of bacterial infection and it becomes larger in size.
Milia
Newborn infants and young children are more commonly affected by milia, which is characterized by formation of very small solid white bump on the eyelid. This happens when the child’s skin is not able to get rid of dead cells in the way it should be. If it occurs in adults, the causes are eyelid trauma or severe sunburn.
Xanthelasma (Fatty Deposits)
Xanthelasma are fatty deposits on the eyelids that occur as a result of aging. They can also indicate that your level of bad cholesterol is too high. They do not produce any additional symptoms.
Papilloma (Infection with HPV)
White bumps on eyelids can develop due to HPV infection. The bumps can grow and become large in size and may require surgical removal in case they affect vision.
Allergies
A white bump on the eyelid can appear due to exposure to allergens. If there are other symptoms including swelling of eyelids, swelling of throat leading to constriction, emergency treatment may be required.
Other Causes
There are certain other causes that may result in the formation of white bumps on the eyelids. Dry eyes could lead to white bumps and it happens when the glands stop secreting oils. Certain conditions such as cellulitis, conjunctivitis, dermatitis, bacterial infections and psoriasis can also result in white bumps. Pimples may also form if you are not getting proper sleep, eating greasy or spicy food or taking certain medicines.
How to Treat White Bumps on Eyelids
Warm Compress
It can decrease the discomfort and pain caused by the bumps. You can repeat the process several times in a day.
Cold Compress
Application of cold compress is advised when the affected area is warm to the touch. This leads to constriction of blood vessels, thereby, decreasing inflammation. Do not apply ice directly to the affected area as this will worsen the condition.
Home Care
Avoid contact the eyes with your hands. If required, ensure to wash your hands properly before touching your eyes.
Maintain hygiene while using contact lenses.
Don’t share your cosmetics and make ups.
Apply a clean washcloth soaked in water on the affected area. You can apply this for 5 minutes, 4-6 times a day. This will decrease pain and shrink the bump.
Avoid squeezing the chalazion or stye. This can spread the infection even to the other eye.
Surgical and Medical Treatment
To treat bacterial infection, antibiotic ointment or eyedrops may be prescribed.
If the stye occurs frequently for many months, an antibiotic cream may be prescribed by your physician to inhibit continuous onset.
Bumps from milia may require topical retinoids, which contain vitamin A. Moreover, surgical procedures such as destruction curettage, diathermy or deroofing may be used.
Papilloma may need surgical excision.
A steroid injection in the affected area may be required to reduce inflammation.
View All Comments /Add Comment