Having pain behind knee after running can indicate more serious medical problem such as a Baker’s cyst or tendinitis. If you notice such pain, stop running to avoid further injury. Treat with ice, elevation and compression of your knee. If there is persistent pain, contact your physician.
Reasons for the Pain Behind Knee After Running
Tendinitis
Your popliteal, calf and hamstring tendons are behind your knee and directly above your calf. The inflammation of these or tendinitis can be caused by over-training, or increasing your speed or distance of running too quickly. Tendinitis can also occur due to tight muscles. Symptoms of tendinitis are knee stiffness, pain and swelling. If ignored, tendinitis can result in small tears in the respective tendons, weakening them, thereby increasing the risk of a complete rupture.
Strain of Popliteal Muscle
Popliteal muscle is a small muscle situated behind your knee and directly above your calf. Unexpected tears can occur in this muscle due to strenuous activities such as downhill running. Its symptoms are swelling, muscle weakness, pain and pressure behind the knee. Symptoms are worsened by running and other high impact activities.
Baker’s Cyst
Bursa sacs and synovial fluid are present in and around your knee joint to help in smoothing movement of the knee. A Baker’s cyst, also referred to as Popliteal cyst, occurs when excessive amount of synovial fluid gets accumulated in the bursa sac present behind your knee. Its symptoms are pain, stiffness and swelling. A noticeable bulge may also be present at the back of the knee.
Hamstring Injury
Hamstring injury is a common cause of pain behind knee after running and occurs when one or more of the three muscles that are present at the back of the thigh gets strained, pulled or injured. Its causes are initiating running activity or quick acceleration activities while running.
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
Patellofemoral pain syndrome, also referred to as runner’s knee, occurs when the femur grove or thighbone is irritated by an unaligned kneecap or patella. Its causes are injury, overuse, excess weight, unaligned kneecap or changes under the kneecap.
Tumors
Pain behind knee may also occur due to benign bone tumors such as osteochondromas, non-ossifying fibromaunicameral bone cysts, fibrous dysplasia, giant cell tumors, and enchondromas. Cancerous tumors that may cause pain behind knee include osteosarcomas and bone tumors caused by Ewing’s sarcoma or multiple myeloma.
Additional Causes
Some of the additional causes of pain behind the knee and above the calf are a meniscus tear, nerve impingement, and knee arthritis and artery entrapment. A meniscus tear is characterized by tearing of the cartilage of the knee and in arthritis, the cartilage wears away. In arthritis and meniscus tear, a symptom of grinding of knee with movement is also experienced. Artery entrapment and nerve impingement occur when blood vessels or nerves are compressed behind your knee. Apart from knee pain, the other symptoms of compressed arteries or nerves are muscle weakness and numbness in your calf and knee.
Complications of Pain Behind Knee After Running
There are immense complications of poorly managed or untreated pain behind the knee. Some of the common complications are listed below:
Difficulty in performing activities of daily living as the mobility is limited.
Limited range of motion and stiffness that may worsen over time.
Overlying skin may get discolored.
Soreness or hypersensitivity of the skin of the entire lower limb.
Pain, swelling, weakness and edema.
Remedies to Relieve Pain behind Knee
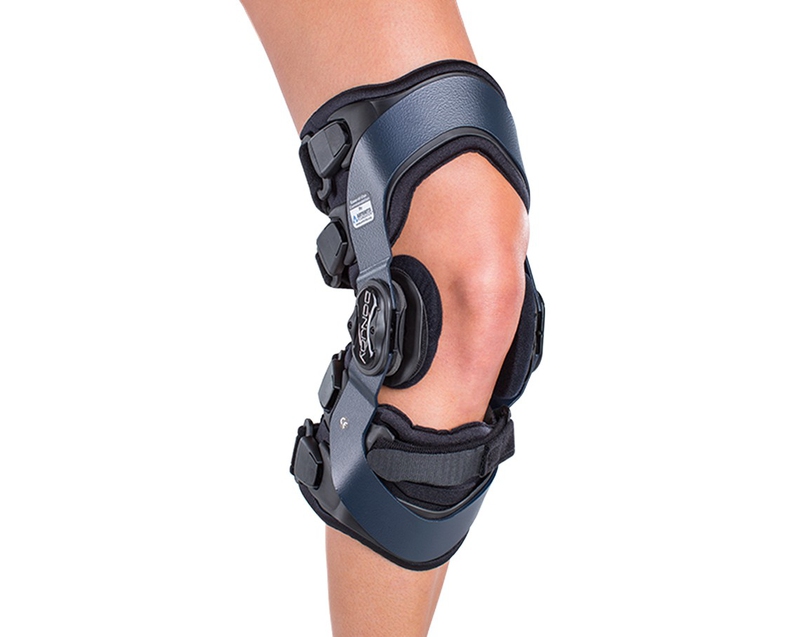
Use Knee Braces
Rest and limited mobility are helpful to relieve pain behind knee, nut knee braces is highly recommended to help in stabilizing the connective tissue and ligaments, thereby, decreasing the symptoms of stress and strain.
Do Stretching Exercises
Low frequency and low impact exercises help in the promotion of blood flow to the healing knee joint. They also promote conditioning of connective tissue and knee muscles. However, the delicate tissues of joint must not be overexerted. Stabilizing and strengthening exercises prevent recurrence of similar symptoms and also improve endurance.
Wear Special Shoes
Many a time, wearing wrong shoes may exert pressure on the knee joint and result in degenerative changes in the articular tissues and connective tissues of the lower limb. Hence, always use right type and right size of shoes as it helps in reducing the strain and stress on your tissues.
Take OTC Drugs
OTC pain killers such as NSAIDs are quite helpful in reducing the symptoms of pain. However, without any clear reason, it is advised to avoid anti-inflammatory medicines and blood thinner without consulting your doctor.
Lose Excess Weight
Being overweight or obesity increases the pressure and stress on your lower limbs and causes a delay in healing. Moreover, degenerative changes are more severe in obese people because of increasing destruction of bone and articular cartilage damage.




View All Comments /Add Comment